10 October, 2022
What is Satellite Imagery?
What is satellite imagery?
Satellite imagery refers to the process of capturing visual data of the Earth's surface from satellites orbiting our planet. These satellites are equipped with specialised cameras and sensors that capture high-resolution images of the Earth's surface, which are then transmitted back to Earth for analysis. The images can range from panchromatic to multi-spectral images capturing a wide spectrum of data.
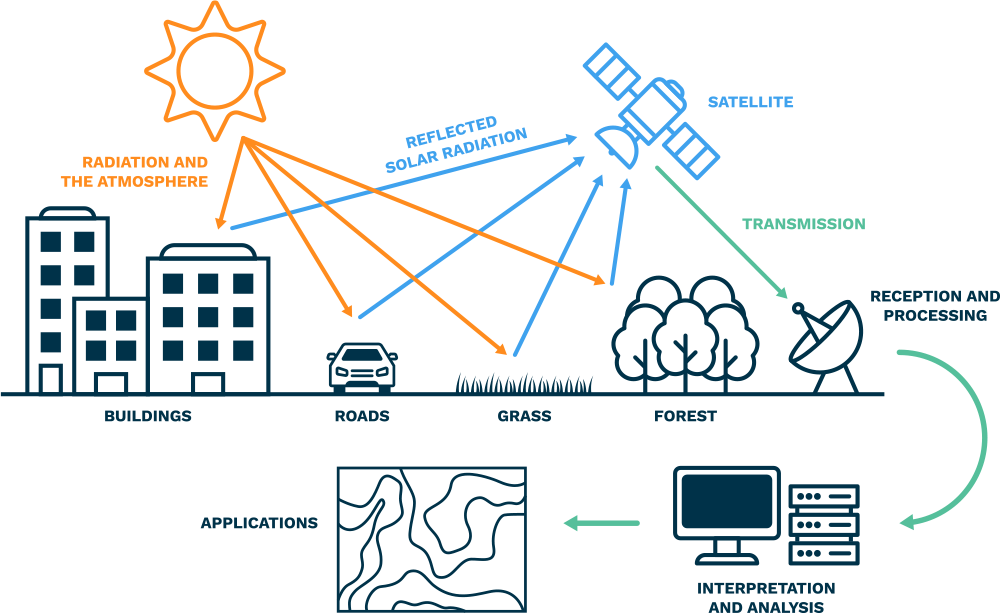
How does satellite imagery work?
Satellite orbit
Satellites can be deployed in various orbits depending on their purpose. Polar orbits (which pass over the Earth's poles) and geostationary orbits (which remain stable over a certain location on the Earth's surface) are two typical types of orbits for Earth-observing satellites.
Data capture
When a satellite passes over an area, its sensors collect information in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The type of data obtained is determined by the onboard sensors. Optical sensors, for example, catch visible and infrared light, but microwave sensors can penetrate clouds and collect data regardless of weather conditions.
Data transmission
After collecting data, the satellite transmits it back to Earth through radio waves. The information is often transmitted to ground stations or receiving antennas on the Earth's surface. These ground stations are deliberately placed across the world to guarantee that the satellite remains in constant contact with it.
Processing
The raw data from satellites is processed to produce useful imagery and datasets. This includes several procedures, including calibration, atmospheric interference correction, and georeferencing to provide geographic locations to the images.
Uses of satellite imagery
Satellite imaging has a wide range of uses, contributing to a better knowledge of our planet. Here are a few examples:
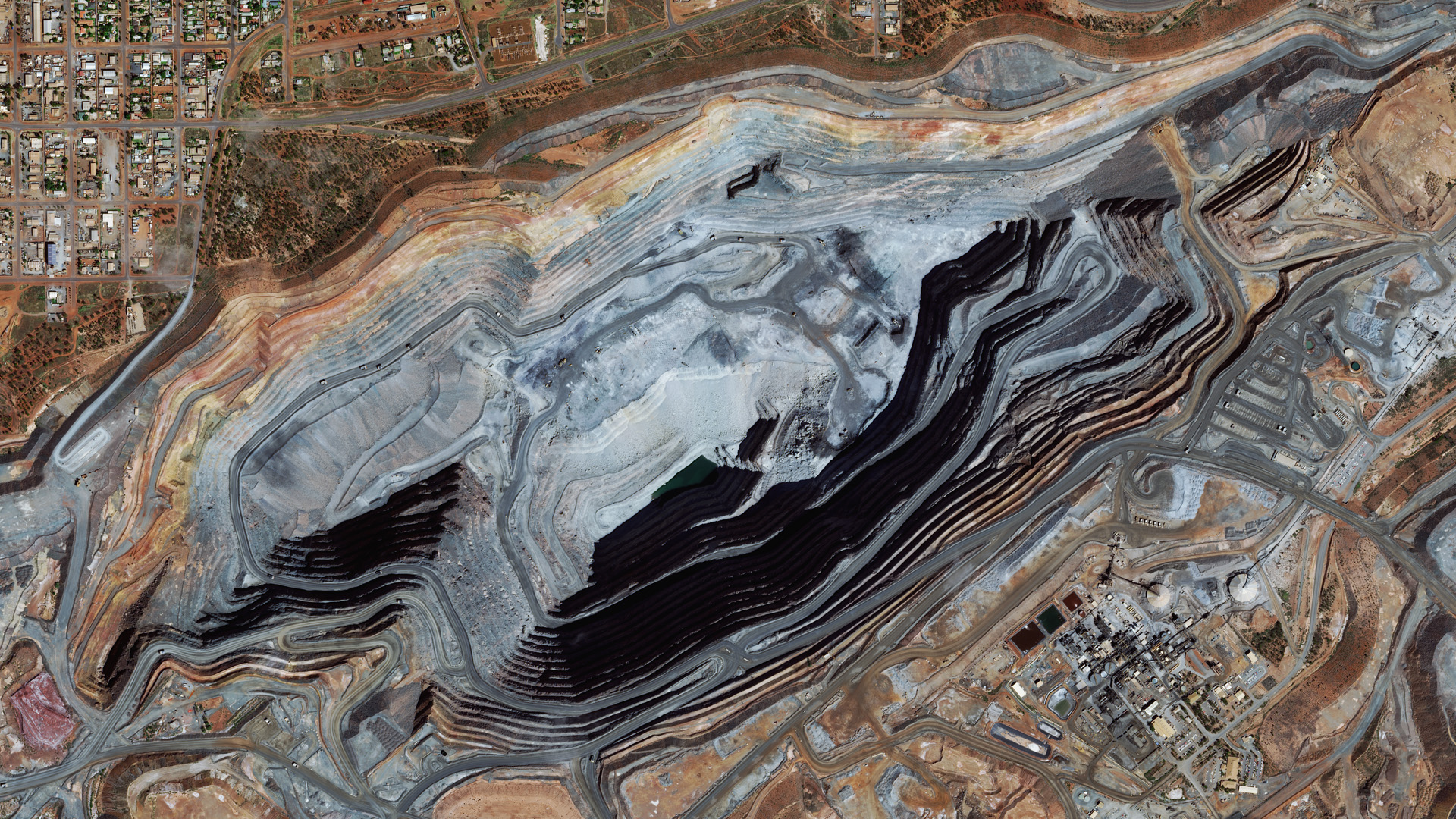
Mining and exploration
- Tailings dam monitoring.
- Exploration for critical minerals.
- Monitor mining site changes and reclamation efforts.

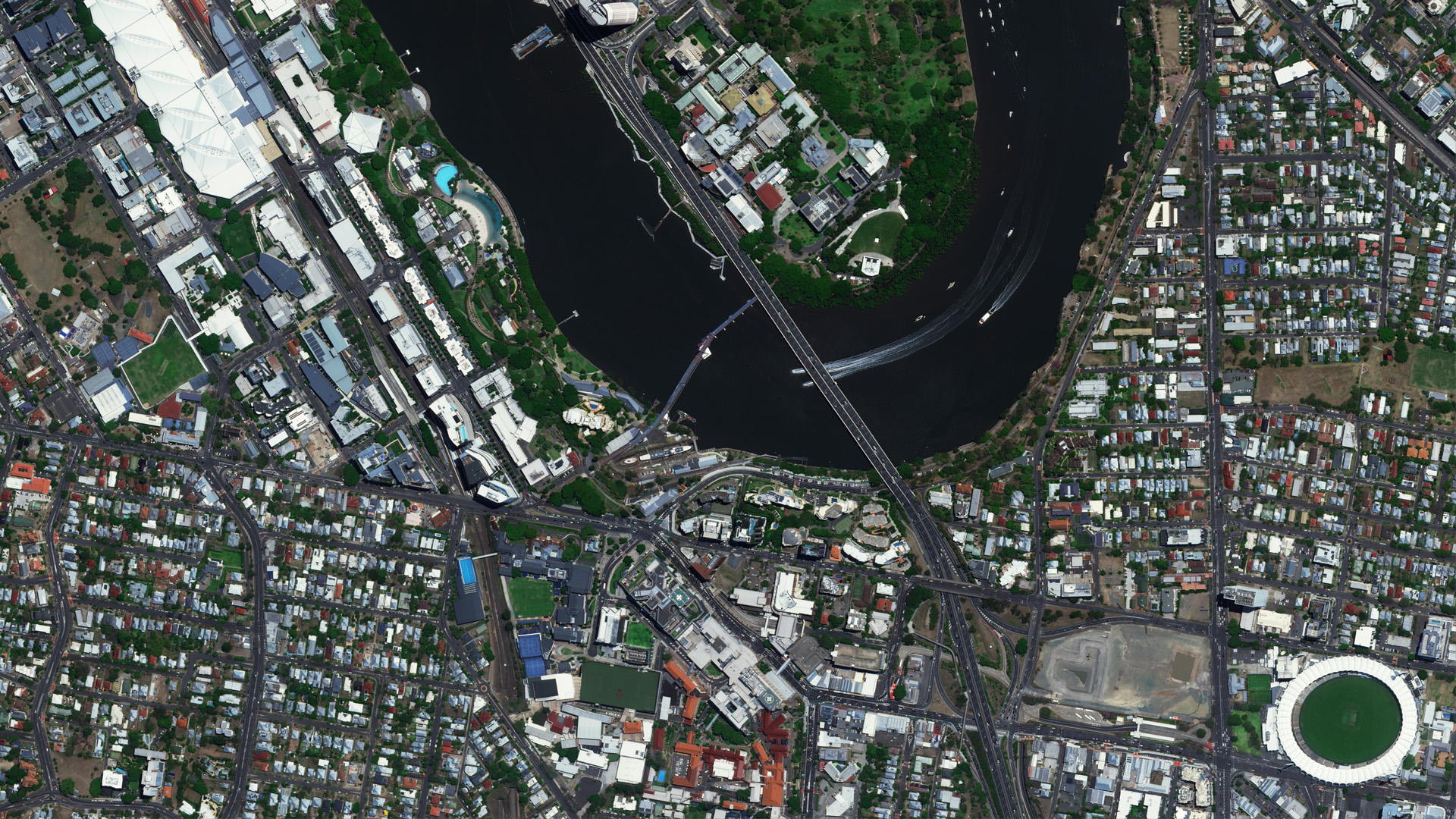
Government
- Large-scale state-wide mosaics.
- Change detection and land use compliance.
- Disaster response and management.
Infrastructure
- Monitor the condition of infrastructure such as bridges, dams, pipelines, and power lines.
- Urban planning and development.
- Transportation and traffic management.
Environmental
- Tracking deforestation and forest health.
- Studying weather patterns and climate change.
Agriculture
- Assessing crop health and predicting yields.
- Identifying pest and disease outbreaks.
Natural disaster management
- Predicting and monitoring bushfires and flood events.
- Providing real-time data for disaster response and recovery efforts.

Advantages of satellite imaging
Satellite imaging has several advantages, making it an important tool for a wide range of applications:
- Global coverage: Unlike limited-range drones or planes, satellites provide comprehensive global coverage, making them excellent for monitoring large-scale events.
- Consistency: Data is collected consistently over time, enabling the monitoring of long-term changes and trends.
- Cost-Efficiency: Satellite imagery is cost-effective, accessible, and avoids high upfront expenses associated with drones and aerial options.
- Safety and accessibility: Satellites improve safety by decreasing the need for on-site data gathering in dangerous or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Historical and archive data: Satellites provide an extensive historical database for long-term trend analysis in areas like environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster management.